Mastering SAP Data Management: From Data Types to Tables and Structures
1.Types of SAP data :-
-
Master data :- A type of data which is accessed very frequently, but changed very rarely.
-
Transaction Data :- A type of data which is always changing and number of records are continuously increasing.
-
Configuration Data :- A type of data which we can customize. Customizing depends on the business scenario and customer requirements.
Examples :- Suppose there is a company ABC.
- Master data :- Employee data of the company ABC.
- Transaction Data :- Transactions in the company ( Banking transactions , Revenue transactions ).
- Configuration Data :-
- (Employee Designation) :- Senior Consultant ( Vehicle allowance applicable )
- (Employee Designation) :- other than Senior Consultant ( Vehicle allowance not applicable).
Data Class :-
- A portion or physical area of the database where table will be stored.
Delivery Class:-
- It is used for controlling data transport of tables during installation, upgrade and transporting between customer systems.
2. Creating Order Item Table:-
-
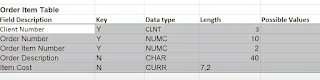
As you know, we have created a order header table in our previous blogs, now we will create a order item table with the following fields.
-
Since we had already created a domain for order number and total amount in the header table, So we will not create it again.
-
So, we just need to create domain for Order item number which is NUMC 2 length and for Order Description which is CHAR 40 length.
-
Similarly, we will create data element for the above two domains and we will start creating the tables.
-
We had already created the header table, so I don’t think it will cause any problem to anyone for creating the item table.
- We will have to assign the currency/quantity field for CURR data type used in ZAR_TOTAL AMOUNT
- Activate the table.
-
3. Creating a Foreign key relationship between Header and Item table :-
- We need to make sure we can only add those data in table ZAR_ITEM which are present in the primary key of ZAR_HEADER table.
Pre-requisite for Foreign key relationships:-
- Tables should have a common key.
- Our Common key between both tables is Order Number.
Assigning the foreign key relationships :-
-
Step 1:- Click on the foreign key button after selecting the order number field in ZAR_ITEM table.
-
Step 2 :- Give ZAR_HEADER in check table and click on create Proposal.
-
Step 3:- Assign cardinality as 1 : N so that we can enter multiple data in item table and click on copy and activate the table.
- Cardinality :- Number of records in key table , corresponds to how many number of records in to secondary/foreign key table.
4. Filling Data in the Order Item table :-
-
Create a TMG for user entries in table same as we did in Order header table.
-
After creating the TMG, go to SM30 and enter the following data.
Note:- We only have 1 to 5 data in the in the order number of Order header table, so we can only enter data between them. For practice purpose please try to enter a numeric value greater than 6.
5.Types of SAP Database Tables :-
- Transparent table
- Pooled table
- Cluster table
1.Transparent Table :-
In case of transparent table, there is 1:1 relationship between ABAP dictionary and the database.
2.Pooled Table :-
- In case of pooled table, there is N:1 (many to one) relationship between the ABAP dictionary and the database.
- For pooled tables, primary-foreign key relationship is not required.
- Table pool structure - Tabname Varkey Dataln Vardata
3.Cluster Table :-
- In case of cluster table, there is N:1(many to one)relationship between the ABAP dictionary and the database.
- For cluster tables, primary-foreign key relationship is mandatory.
- Table cluster structure - Key Pageno Vardata
6. Structures :-
- Structure is a collection of fields/columns of different data type or similar data type.
- Structure does not contains any data.
- Structure does not have any primary key
Types of Structures :-
1. Include Structure :-
- It is a reusable structure.
- We can insert the include structure at any point.
- It is applicable to customer specific tables, It is not applicable to SAP specific tables.
2. Append Structure :-
- It is not a reusable structure.
- It always inserts at the last.
- It is applicable to both customer specific tables and SAP tables.
We will create the include and append structure in the order header and order item table in the next blog :-










.png)

.png)
Comments
Post a Comment