Mastering Debugging Techniques: From Breakpoints to Watchpoints
- Debugging is a technique by which we can find the error, Correct the error and detect the error.
- Always prefer Desktop 3, as it provides more space to see the data more clearly.
Ways of Debugging :-
-
Put the breakpoint on any executable statement and program will automatically stop at that point.
-
Any statement that perform some execution is term as executable statement.
-
Note :- The program must be in active state to put a break point on it.
-
-
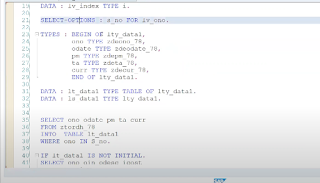
We can debug the code with the help of transaction code /h.
Execution keys in Debugging :-
- F5 - Step by Step Execution: Executes the program one line at a time, allowing you to step through each line of code, including stepping into function calls for detailed inspection.
- F6 - Line by Line Execution: Similar to F5 but skips over function calls, executing only the current line of code and moving to the next line.
- F7 - Return: Steps out of the current function, allowing you to quickly return to the calling function's context.
- F8 - Continuous Execution or Exit: Resumes continuous execution of the program until the next breakpoint is encountered or until the program completes. Can also be used to exit debugging mode.
System Variables in Debugging Mode :-
-
SY-SUBRC and SY-TABIX system variables are by default present in the debugging mode.
-
In SY-SUBRC, RC stands for return code
- If SY-SUBRC = 0 { Operation Successful }
- If SY-TABIX = 0 {Operation Unsuccessful }
-
SY-TABIX :- It always works inside the loop and gives us the index of the row i.e. if first row is inside the loop, then SY-TABIX = 1 and so on.
Static and Dynamic Breakpoint in Debugging :-
-
Static breakpoints are user independent break - points , that means they are not dependent on users.
- For, example :- Suppose, There are two users :- User 1 and User2 . So, If User 1 will put a static break point, then User 2 will also go into debugging mode.
Syntax :-
- BREAK-POINT.
-
Dynamic breakpoints are user dependent breakpoints, they do not affect other users.
Syntax :-
- BREAK - User name
Various Features in Debugging Mode for Internal Tables :-
-
Change the contents of selected rows.
-
Delete Selected rows.
-
Delete all rows ( Delete complete table ).
-
Append Row.
Deleting and Deactivating Breakpoints :-
1. Deactivating Breakpoint :-
-
It is to temporary deleting the break-points in that particular session and when the program again runs, the breakpoints will be there.
2. Deleting Break-Point :-
-
Permanently deleting the break-points.
Watchpoint :-
-
A watchpoint is used to monitor the values of variables and Internal tables, Work areas etc.
- Click on watchpoint.
- Provide the variable on which you want to put the watchpoint.
-
When data will change in the internal table, you will get a notification.










.png)

.png)
Comments
Post a Comment